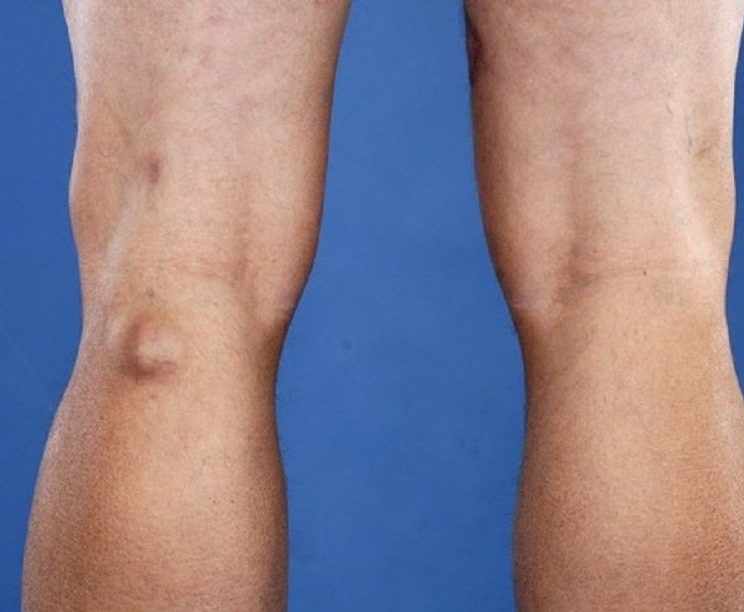
Baker’s Cyst (Popliteal Cyst)
What is a Baker’s cyst?
A Baker’s cyst is a pocket of fluid that forms a lump behind the knee. It is also called a popliteal (pop-luh-TEE-ul) cyst, and is usually the result of a problem with your knee joint, such as arthritis or a cartilage tear. Both conditions can cause your knee to produce too much fluid, which can lead to a Baker’s cyst.
What causes a Baker’s cyst?
A Baker’s cyst is caused when excess joint fluid is pushed into one of the small sacs of tissue behind the knee. When this sac fills with fluid and bulges out, it is called a cyst. The excess fluid is usually caused by conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis that irritate the knee. It may also be caused by an injury.
What are the symptoms?
Often a Baker’s cyst causes no pain. When symptoms occur, they may include:
- Tightness or stiffness behind the knee.
- Swelling behind the knee that may get worse when you stand.
- Slight pain behind the knee and into the upper calf.
You are most likely to feel this when you bend your knee or straighten it all the way.
Sometimes the pocket of fluid behind the knee can tear open and drain into the tissues of the lower leg. This can cause swelling and redness in that part of the leg.
Rarely, a Baker’s cyst bursts and synovial fluid leaks into the calf region, causing:
- Sharp pain in your knee;
- Swelling in the calf;
- Sometimes, redness of your calf or a feeling of water running down your calf.
These signs and symptoms closely resemble those of a blood clot in a vein in your leg. If you have swelling and redness of your calf, you’ll need prompt medical evaluation to rule out a more serious cause of your symptoms.
Diagnosis
A Baker’s cyst can often be diagnosed with a physical exam. However, because some of the signs and symptoms of a Baker’s cyst mimic those of more-serious conditions, such as a blood clot, aneurysm or tumor, your doctor may order non-invasive imaging tests, including:
- Ultrasound
- X-ray
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Treatment
If required, treatment usually involves treating the underlying condition. Other options include injection therapy, fluid drainage with a needle or physiotherapy.
Sometimes a Baker’s cyst will disappear on its own. However, if the cyst is large and causes pain, your Podiatrist may recommend the following treatments:
- Medication. Your Podiatrist may inject a corticosteroid medication, such as cortisone, into your knee to reduce inflammation. This may relieve pain, but it doesn’t always prevent recurrence of the cyst.
- Fluid drainage. Your Podiatrist may drain the fluid from the knee joint using a needle. This is called needle aspiration and is often performed under ultrasound guidance.
- Physical therapy. Icing, a compression wrap and crutches may help reduce pain and swelling. Gentle range-of-motion and strengthening exercises for the muscles around your knee also may help to reduce your symptoms and preserve knee function.
- Reduce your physical activity. Doing so will reduce irritation of your knee joint. Your Podiatrist can offer you guidance on how long you need to reduce your activity levels, and he or she may be able to suggest alternative forms of exercise you can do in the meantime.
If possible, Podiatrists treat the underlying cause of the cyst. If your Podiatrist determines that a cartilage tear is causing the overproduction of synovial fluid, he or she may recommend and refer for surgery to remove or repair the torn cartilage.
Baker’s cysts associated with osteoarthritis usually improve with treatment of the arthritis. Surgical intervention is rarely needed.
At the Foot and Ankle Clinic our highly qualified team of Podiatrists are all members of the Australian Podiatry Association and offer a combined 50 years’ experience. They are trained to diagnose and effectively treat Baker’s Cysts via a range of proven treatments.
Put your feet in our hands! See us today in Chadstone, East Bentleigh, Moe, Sale, Traralgon, Warragul & Online Store and Retail Enquiries. NO REFERRAL NEEDED!.